Biodiverciti
What role can you play in the biodiversity and climate crisis - in the familiar surroundings of your own garden? Citizen scientists implement biodiversity-enhancing measures in their garden, observe animals and plants and are analyzed how their attitudes and behaviors change.
What are the aims of the project?
BIODIVERCITI pursues two core research questions to analyze the impact of its intervention on Citizen Scientists and their gardens: 1. What improvements can be achieved in indicator species? BIODIVERCITI analyzes the effectiveness of adapted gardening and cultivation practices to increase biodiversity. 2. How do individual climate action and efficacy beliefs change? By transforming their own gardens, citizen scientists can develop a sense of control, even if they feel overwhelmed in the face of global crises. In contrast, experiencing personal limitations in achieving quick ecosystem improvements or feeling that they have “already done their part” can undermine subsequent climate action efforts.
How can you participate in research?
Citizen Scientists can participate in BIODIVERCITI by...
- implementing biodiversity-enhancing measures in their own garden
- observing and reporting selected indicator species
- actively exchanging information on implementation and observations with other citizen scientists and the project team
- taking part in seminars and network meetings for improving their personal knowledge and for discussing project results
- taking part in surveys on attitudes and behavior

Octopus Den Initiative
How do octopuses use the artificial octopus dens near the Croatian island of Krk, and what can be studied with them? Film or photograph them during your next dive or snorkeling trip to contribute to octopus research!
What are the aims of the project?
The project investigates whether and to what extent wild octopuses adopt artificial octopus dens and which factors influence their choice. Additionally, it examines in which areas they are found, which types of seabed they prefer, and what behaviors they display there. A key objective is to analyze the octopuses' preferences for specific designs and locations of artificial dens. This not only helps to better understand their natural behavior but also promotes the development of new research methods for studying octopuses in the wild and supports the conservation of these intelligent animals. Moreover, the artificial dens provide a unique opportunity to explore the cognitive abilities of these fascinating marine creatures in greater detail.
How can you participate in research?
Divers and snorkelers can take part in the Citizen Science project 'Octopus Den Initiative' by visiting the artificial octopus dens near the island of Krk during their private dives or snorkeling trips (e.g., while on vacation) and observing and documenting what they see. Especially helpful are photos and videos of the artificial dens — whether they are occupied by octopuses or empty. Photos and videos of octopuses found outside the dens are also valuable. The collected photos and videos can easily be shared with us, for example, via email or through our social media channels (e.g., Facebook). Every observation helps us learn more about the behavior and distribution of octopuses in this area. All important information about how to participate, as well as guidelines, can be found on our website.
Pictures
-
 Octopus in the artificial octopus cave H1 Punat lighthouse Octopus in the artificial octopus cave H1 Punat lighthouse
Octopus in the artificial octopus cave H1 Punat lighthouse Octopus in the artificial octopus cave H1 Punat lighthouse -
 Diver at the artificial octopus cave H7 Sv. Marak Diver at the artificial octopus cave H7 Sv. Marak
Diver at the artificial octopus cave H7 Sv. Marak Diver at the artificial octopus cave H7 Sv. Marak -
 Map of the artificial octopus caves (as at 12 March 2025) Map of the artificial octopus caves (as at 12 March 2025)
Map of the artificial octopus caves (as at 12 March 2025) Map of the artificial octopus caves (as at 12 March 2025)
https://www.citizen-science.at/en/conference/tag/animals#sigProId73dd95bc0b

BIOM-Garten
Monitoring of Amphibians and Reptiles in Austrian Gardens
The BIOM-Garten project invites people of all ages to look out for amphibians and reptiles in their gardens and report their observations. This will help to fill gaps in existing monitoring and implement better conservation measures for these endangered animals.
What are the aims of the project?
Amphibians and reptiles are among the most endangered animals in the world. In Austria, more than half of the 21 amphibian and 15 reptile species are classified as endangered, critically endangered or already threatened with extinction. The aim of the project is to fill the gaps in the existing monitoring of amphibians and reptiles with the help of citizens and to shed more light on private gardens as habitats for endangered species. In addition, citizens can describe their gardens to characterise environmental parameters, and remote sensing methods will be used to complement species monitoring. This is the first time that the contribution of gardens to habitat connectivity is analysed specifically for aquatic and semi-aquatic animal groups. The garden descriptions will also help to identify structures that are most favourable for particular species.
How can you take part in the research?
Monitoring made easy! Use your favourite app. The website artenzählen.at, which has been specially designed for amphibian and reptile monitoring, allows you to create species reports and garden descriptions in just a few clicks. Photos of all native species and intuitive input options make reporting easy. If you are already reporting frogs, lizards etc. on Naturbeobachtung.at, iNaturalist or Herpetofauna.at, you can continue to do so, as observations from these platforms will also be included in the overall results of the BIOM-Garten project. However, it is important that you mention 'BIOM-Garten' in the comment field so that the sightings can be correctly categorised. And please do not forget the garden description on artenzählen.at.
Picture gallery
-
 Eastern Green Lizard Eastern Green Lizard
Eastern Green Lizard Eastern Green Lizard -
 Common Toad Common Toad
Common Toad Common Toad -
 Aesculapian Snake Aesculapian Snake
Aesculapian Snake Aesculapian Snake -
 Yellow-bellied Toad Yellow-bellied Toad
Yellow-bellied Toad Yellow-bellied Toad -
 Fire Salamander Fire Salamander
Fire Salamander Fire Salamander -
 Slow Worm Slow Worm
Slow Worm Slow Worm -
 Grass Snake Grass Snake
Grass Snake Grass Snake -
 Tadpole of the Common Tree Frog Tadpole of the Common Tree Frog
Tadpole of the Common Tree Frog Tadpole of the Common Tree Frog -
 Common Frog Common Frog
Common Frog Common Frog -
 Spawn of the Agile Frog Spawn of the Agile Frog
Spawn of the Agile Frog Spawn of the Agile Frog
https://www.citizen-science.at/en/conference/tag/animals#sigProId2bce82b18c
Videos
Explanatory video (in German)
Webinar: Discover the fascinating world of amphibians (in German)
Webinar: Discover the fascinating world of reptiles (in German)
Partners
.png)
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Phänologie - Naturkalender - Phenowatch
Since 1851, we have been researching the changes in weather, climate and nature and what this means for us humans by observing plants and animals. These phenological observations help, for example, in climate research, agriculture and pollen forecasting in order to better deal with climate change.
What are the aims of the project?
Plants act as an integrating measuring instrument for a variety of environmental factors such as weather conditions in the past and current vegetation year. If one analyzes the temporal course of phenological observation data, the influencing factor of air temperature becomes clear, especially in the spring phases in Austria, both in short-term fluctuations and in long-lasting trends. Phenology is therefore an ideal bio-indicator for gradual changes in the climate. Research objectives include
- Climate monitoring in addition to instrumental measurements.
- Temperature sensitivity of phenological events - Does the sensitivity of plants change with the temporal shift of phenological phases?
- Groundtruthing of vegetation indices from satellite observations.
- Further basic plant physiological research - future phenological modeling on an even more plant process-oriented basis.
How can you participate in research?
Find your favorite trees and shrubs in your favorite location and observe and document their development from bud burst and the start of flowering to fruit ripening, leaf coloration and leaf fall through the ten phenological seasons. We are looking for the date for the start of the respective development phases of the so-called indicator plants. You can send this to us in the "Nature Calendar" app with a photo or in the traditional way using a paper form. You can find all the information you need on our website.
-
 Important indicator plants Important indicator plants
Important indicator plants Important indicator plants -
 Snowdrop blossom Snowdrop blossom
Snowdrop blossom Snowdrop blossom -
 Black elderberry Black elderberry
Black elderberry Black elderberry
https://www.citizen-science.at/en/conference/tag/animals#sigProId2b82b6fefd
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Butterfly Monitoring Austria
Many people in Austria feel that colorful butterflies are becoming increasingly rare. Unfortunately, this is also reflected in the European Grassland Butterfly Index, compiled by Butterfly Conservation Europe from datasets across the continent. Since 1990, typical grassland butterflies have declined by 36%.
Since butterfly populations naturally fluctuate from year to year, only long-term standardized monitoring can determine whether numbers are increasing or decreasing. To enable this, the initiative “Austrian Butterfly Conservation” (ABC) was established in Austria.
Where are butterflies counted?
In short: anywhere that interests you. You can count butterflies in your own garden or along a public walking path, for example. The key is to count only those butterflies flying within 5 meters in front of you or 2.5 meters to your left and right. If the observation area is large enough to walk at least 50 meters in one direction, you can even conduct a “transect survey,” which is the international gold standard.
This year, we are especially excited about observations in towns with more than 10,000 inhabitants!
When are butterflies counted?
The highest number of species and butterflies can typically be observed in July and August. If you enjoy counting, we would particularly appreciate additional observations at one- to two-week intervals. If a butterfly species is recorded at the same location three times in a year, the data can already be used to calculate the Grassland Butterfly Indicator!
Participate in four steps
- Register at „Austrian BMS“
- Install the ‘Butterfly Count’ app (available for iOS and Android)
- Familiarise yourself with butterfly species (identification aids and tips at: Links & Downloads | Austrian Butterfly Conservation )
- Observe butterflies in the garden or another location for 15 minutes in fine weather and enter them directly into the app (German or scientific name)
And don't worry, if you don't know the species, you can still enter the family 'white butterfly' or 'blue butterfly'. The more you go out, the more familiar you will become with your butterflies and you are sure to come across a surprise or two in the insect world.
Often it is necessary to catch the animals in order to identify them, as nature conservation laws vary from country to country. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.
We at ABC would be delighted if you would like to become part of the butterfly monitoring programme and hope you have fun observing and counting! If you have any questions or comments, please email us or visit our website.
-
 Butterfly identification guide Butterfly identification guide
Butterfly identification guide Butterfly identification guide -
 Documentation in the field Documentation in the field
Documentation in the field Documentation in the field -
 Identification workshop Identification workshop
Identification workshop Identification workshop -
 App for data collection App for data collection
App for data collection App for data collection -
 Excursion; (c) K. Zalneva Excursion; (c) K. Zalneva
Excursion; (c) K. Zalneva Excursion; (c) K. Zalneva -
 Hauhechel blue (the underside is important for identification) Hauhechel blue (the underside is important for identification)
Hauhechel blue (the underside is important for identification) Hauhechel blue (the underside is important for identification)
https://www.citizen-science.at/en/conference/tag/animals#sigProIdeb1e0c0615
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Bug us with your ticks!
For our national tick monitoring programme, we invite you to provide us with ticks. Your samples will help us analyse which tick species appear when and where in Austria. Moreover, ticks will also be investigated for the presence of pathogens.
What are the aims of the project?
The goal of our national tick monitoring programme is to obtain data regarding tick species in Austria, their occurrence, and the pathogens they may carry. The objective is to sample ticks from a wide variety of regions, regardless of whether they are sourced from vegetation or hosts. The collection of ticks is mainly conducted by citizen scientists, whose participation is essential for the success of such an initiative. The collected data can assist in identifying hot spots for specific pathogens, discover new or lesser-known microorganisms, and learn about the occurrence of native tick species but also the spread of invasive ones such as Hyalomma. A continuous monitoring is of importance particularly in light of climate change which can strongly impact the tick fauna. The insights gained from this programme can enhance overall health by facilitating earlier detection of tick-borne diseases and thereby allowing for timely and appropriate treatment.
How can you participate in research?
As soon as you encounter a tick you can join the project if following pre-requisites are fulfilled:
- Tick still intact (i.e. not squeezed out or badly damaged)
- Data available for:
- Date of tick discovery or removal from host
- Postal code and location
- Host information (if tick was removed from a host – which one?)
Ticks have to be securely packaged (e.g. by adhesive tape on a piece of paper inside a properly closed envelope) before being either dropped off at an AGES location or being sent to Vienna:
AGES GmbH
Department for Vector-borne diseases - Ticks
Währinger Straße 25a
1090 Vienna
We would like to point out that the legal regulations for the transportation of dangerous goods by mail must be observed. Live ticks can only be dropped off at the listed drop-off locations.
Further details can be found on our homepage in the section “Found a tick?”. If you suspect to have found a Hyalomma tick (“giant tick”) without the possibility to submit the tick to us please send a photo to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. Thank you!
Background informationen
So far 19 native tick species have been described in Austria. The most common ones belong to the genera Ixodes (e.g. I. ricinus), Dermacentor (e.g. D. reticulatus) and Haemaphysalis (e.g. Ha. concinna). These hard ticks have a lifecycle which comprises of three life stages (larva, nymph, adult). Between each life stage, and before a female adult tick can lay eggs, a blood meal must take place.
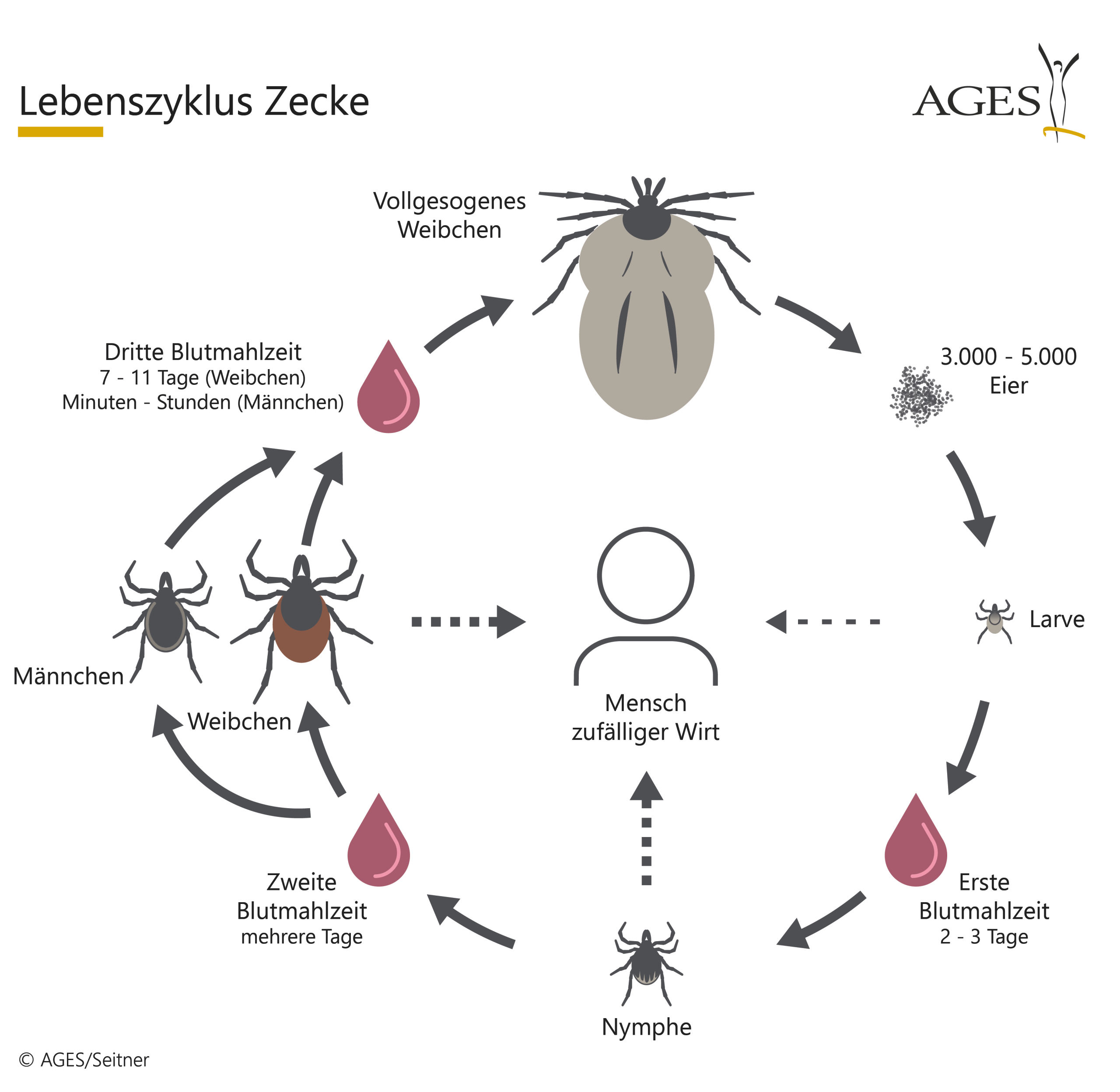
Most pathogens are taken up from reservoir animals during those blood meals (e.g. small rodents, birds, etc.) and can be transmitted from the tick at the next blood meal. The most common pathogen found in ticks in Europe are bacteria of the genus Borrelia which are the causative agent of Lyme borreliosis. However, there are many other tick-borne pathogens which can cause diseases in humans and animals (e.g. Rickettsia, Anaplasma, Neoehrlichia, etc.).
Aside from native ticks the so-called ‘giant ticks’ are increasingly appearing in the media.
They are identifiable by their typical yellow stripes along their legs when compared to native ticks. These ticks are usually imported to Austria from warmer regions. Due to climate change an expansion into more northern regions can be expected. Hyalomma ticks can transmit more harmful pathogens (such as Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus or Rickettsia aeschlimannii) hence, monitoring the spread of this vector is of medical importance. However, this is only possible by reports from well informed citizens. Thanks to citizen scientists we were able to uncover a previously unrecognized way of migration for these ticks: rather than migratory birds, it was tourists who were responsible for a significant number of introductions of Hyalomma ticks to Austria.
To be able to monitor the tick fauna of Austria for health relevant changes (i.e. expansion of dangerous vectors, emergence and spread of (new) pathogens) a national tick surveillance programme was started beginning of 2024 as part of an EU-project (OH SURVector, EU-Project Nr. 101132974). The acquisition of another project allows for continuation of the implemented surveillance activities until end of 2028.
The mission of AGES is to supply citizens with information. For that reason, a homepage is available which features interesting content about ticks and tick-borne diseases. Moreover, detail information about the ongoing surveillance study and its results are provided.
Role descriptions
Within this project four main tasks are executed:
- Tick collecting
- This step is planned to be carried out by citizen scientists. Participation is open to anyone who finds a tick and sends it to AGES where further processing will take place. It is crucial that submitted ticks are intact and the necessary information regarding date, location and hosts is provided.
- Morphological tick identification
- Tick experts will analyse morphological features of the tick under a microscope to determine the tick species. During that, samples are entered into an internal database, and it is decided whether a tick sample is eligible for further analysis. Strongly damaged ticks will not be processed further than this step.
- Molecular screening for pathogens
- In the next step trained laboratory personnel will extract the nucleic acids (RNA and DNA) of the tick sample and perform molecular methods (e.g. PCR) for detection of tick-borne pathogens. The results are then entered into the internal database.
- Results and communication
- The results of the molecular screening and morphological analysis are summarized. A team of tick experts, data experts and communication experts work together in this step to create maps, submit data to international databases, update the homepage or prepare newsletters. Occasionally information may be disclosed to the media.


This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
SoilRise
Monitoring of Soilbiota by Citizen Science
SoilRise is a research project on earthworm biodiversity in Europe. Earthworms play a crucial role in soil fertility and are considered important ecosystem engineers. With your help we like to collect data on the distribution and diversity of earthworms in Europe.
But SoilRise is more than scientific research. We aim to build an interactive network between researches, citizen scientists (you) and stakeholders to raise awareness of the importance of soil biodiversity. We seek to explore, protect and conserve the diverse habitats beneath our feet. By taking part in SoilRise, you will be actively contributing to the preservation of our soils and a positive impact on the environment.
Aims
The SoilRise project aims to improve the availability of data on earthworm populations and raise awareness of the biodiversity found in our soils. We aim to identify threatened or non-native earthworm species and compare traditional identification methods with DNA analysis. We will also look at species diversity in different countries to understand the ecological variation that exists.
What do we offer?
- Education and training: SoilRise offer training courses that teach the basics of soil ecology and sampling. There are also workshops that provide in-depth knowledge about earthworms.
- Engagement and impact: Your participation supports our scientific research project and makes a direct contribution to environmental protection. By sampling at different sites you will increase your knowledge of soil biodiversity.
- Community and networking: Become part of the SoilRise network, sharing ideas and networking with other participants and experts.
- Sampling and effort: Your participation is flexible, you can start, stop and continue as you wish between October 2024 and 2026. The effort per site is about 5h.
- Meet and greet: Discover the soil beneath your feet, meet interesting people and experience nature from a new perspective.
Sampling
Sample your field with a spade during the months of March to May and/or September to November. Sampling takes approximately 5 hours and you can record your data on the form provided or on our website. Our team will help you every step of the way, on site if possible.
We will provide all necessary documents such as sampling instruction and data sheets. Our seminars and webinars will to help you to prepare for sampling and you will learn more about the world of earthworms.
At our networking sessions, we will invite you to share your experiences with other participants and the research team.
Who could participate?
Anyone over the age of 14 can take part in the project and search for earthworms (farmers, gardeners, agricultural schools and everyone who is interested).
We have three categories:
- field (arable fields including large scale vegetable production, viticulture),
- small vegetable beds and flower beds (home garden, community garden, town garden, market gardening)
- lawn/meadow, grassland and green spaces (lawns, natural meadows, agricultural grassland)
It is also possible to take part in the project without having a own plot of land.
Register directly at our project website.
SoilRise is a biodiversa+ project in cooperation with Germany, France, Ireland, Poland and Austria.

This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
DANUBE4all
DANUBE4all is an EU project with the main task of developing a comprehensive action plan for the renaturation of river stretches in the Danube River Basin (DRB). To this end, a collaborative stakeholder process is being developed that actively incorporates the interests of citizens. The action plan is intended to contribute to the improvement of the ecological status, biodiversity and river connectivity of the Danube ecosystems and thus supports the EU mission OCEAN ‘Mission Healthy Oceans, Seas, Coastal and Inland Waters’.
The development and implementation of innovative and socially relevant nature-based solutions has a wide range of positive effects. In addition to the improved connectivity of rivers, possible scenarios for floodplains, reducing the risk of floods and droughts, and other socio-economically effective measures are an important focus. Renaturation projects on the Danube are being promoted with the goal of improving the continuity of sediments and positively influencing habitats/biota. These include the Danube National Park east of Vienna, a section of the river in Hungary and a measure on the Danube delta.
Nature-based solutions must be developed in collaboration with the affected population and supported by them in order to be effective in the long term. Renaturation processes tend to unfold slowly and require continuous attention and active support in order to be successful. Accordingly, the intensive involvement of citizens along the Danube is an important component that makes renaturation possible in the first place. A special work package supports interaction with citizens through the activation of citizen science. Citizen scientists are particularly involved in the development, implementation, evaluation and scaling of nature-based solutions, a citizen science method toolbox, and the development of communication measures.
In particular, DANUBE4all serves the following research fields:
- Criteria and indicators for physical connectivity status as a starting point for renaturation options in the Danube catchment. A reflection of existing assessment methods and initiatives contributes to this.
- Analysing the (ecological) status of water bodies and biodiversity with the aim of expanding the existing transnational biodiversity monitoring with a strong focus on restoration. This includes long-term trends in connection with management and conservation measures associated with renaturation.
- Co-creation, implementation and results monitoring of nature-based solutions implemented in the project in the Danube River Basin. This includes:
- 3 restoration interventions with the participation of local residents (3 Demonstration Sites);
- the further use and replication of solutions in 5 Associated Regions;
- later a multiplication of the approach by supporting 10 restoration measures (10 Synergy Sites).
- Implementation of socially relevant integrative measures with municipalities in the Danube River Basin. This includes measures that trigger social and economic change, as well as the sustainable, integrative and long-term management of restored ecosystems through public mobilisation and engagement. This is also to be achieved through citizen science.
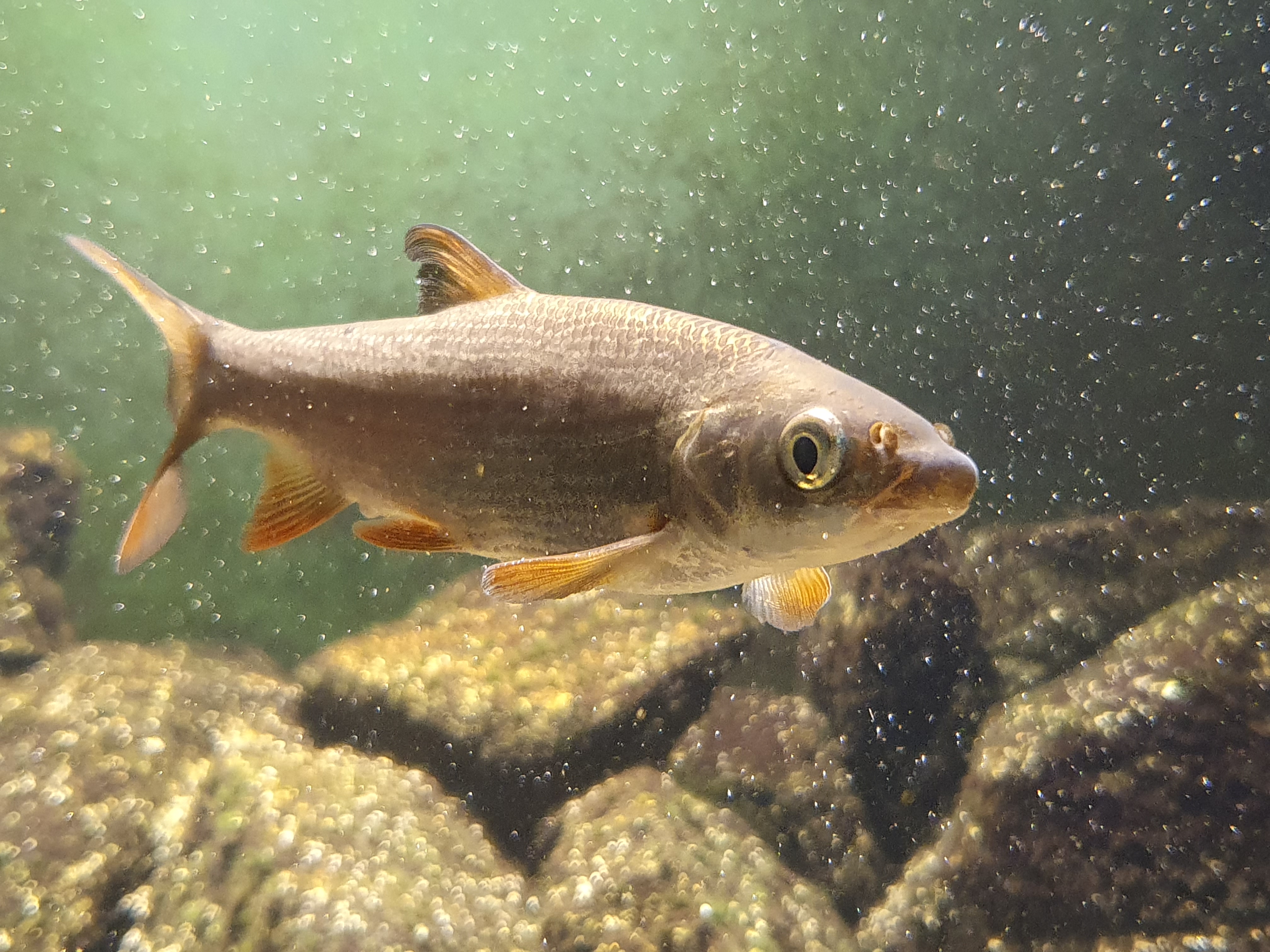

common nase, © Robert Togel (Images courtesy of viadonau)
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
On the trail of springs
Spring habitats in the Großes Walsertal Biosphere Reserve
In view of increasing extreme weather events, including periods of drought and consequent water shortages, the protection and knowledge of springs in the Großes Walsertal Biosphere Reserve is becoming increasingly important. In addition to their essential role in water supply, springs are often small but very important habitats for endangered organisms. The pressure to utilise and develop existing springs has increased significantly due to climate change. In order to raise awareness of these special habitats and obtain an overview of the existing spring habitats in the valley, the KLAR! Biosphärenpark Großes Walsertal is launching a citizen science project in cooperation with Life Science AG.
As an introduction, an online workshop will take place on 18 February 2025 from 19:00 to 20:30. Participants will gain exciting insights into the hidden world of springs, their ecological value for highly specialised species and the importance of certain organisms as indicators of water quality. They will also be shown how climate change and increasing utilisation pressure are affecting these sensitive habitats. Finally, the methodology of spring mapping will be presented and a typical mapping day outlined. After the workshop, interested parties will have the opportunity to secure a place on the field trip in summer 2025, during which the methodology will be applied in the field.
Life Science AG has already successfully carried out a citizen science project to record spring habitats in the Black Forest biosphere area and will now transfer this project to the conditions in the Großes Walsertal. The tried-and-tested mapping and evaluation method records not only the location but also characteristics such as spring size, temperature, cultural-historical significance, flora and fauna as well as potential human influences. As an alternative to the tried-and-tested analogue recording, the Qfield app is also being adapted so that walks in the Großes Walsertal can become small research trips.
As a model region for sustainable development, the biosphere reserve bears a special responsibility for the long-term protection of natural springs. We are committed to securing the supply of drinking water and at the same time protecting the habitat for rare species. At the same time, we must ensure that the springs are utilised in the most environmentally friendly way possible to provide water for humans and animals.
If you are interested, please register in advance with our Klar! manager - Lukas Ellensohn at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.. He will send you all further details and the link to the online workshop.

This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Show me your mouse, cat!
Your cat - our researcher
Attention cat owners in Vorarlberg! Under the motto "Show me your mouse, cat!", we are collecting dead mice and other small mammals that your cat brings to your home. From June to November 2024, you can hand in these "gifts" from your cat to us or other collection points in Vorarlberg. The aim of this campaign is to obtain as much data as possible on our native small mammals for the compilation of the Vorarlberg Red List of Small Mammals.
A project as part of the Vorarlberg Red List of Small Mammals
HOW DO I COLLECT A DEAD MOUSE?
Because dead animals can carry pathogens or parasites, the following principle applies: Do not touch a dead animal with your fingers!
Therefore, please proceed as follows:
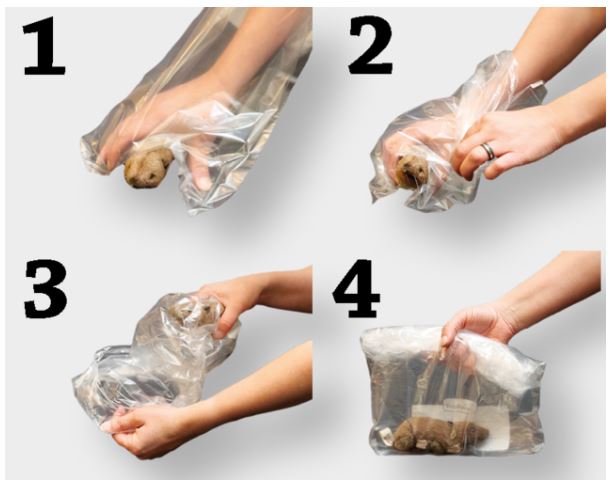

- Take a plastic bag (e.g. freezer bag) and put your hand in it.
- Grasp the dead mouse with your hand in the plastic bag.
- While holding the mouse with one hand, run your other hand along the edges of the bag over the mouse in your hand.
- Use a pencil to write down the following information about the find on a piece of paper: your name, address, telephone number, e-mail address, date or use the form for reporting (in German) a find. Only fully completed forms result in a scientific data record and can/may be recorded.
- Place the slip of paper in the plastic bag with the mouse.
- Seal the plastic bag tightly and in a space-saving manner (no air in the bag if possible)
- Place the plastic bag in the freezer.
- Take the plastic bag to inatura or one of the collection points at the next opportunity. Please do not allow it to thaw (cool bag/box with cool packs).
If you follow this simple method, you are on the safe side.
PLEASE DO NOT SEND THE DEAD ANIMALS BY POST! THE ANIMALS ARE THEN NOT SUFFICIENTLY COOLED AND DECOMPOSE VERY QUICKLY. PLEASE ONLY SEND ANIMALS WITH FUR (NO BIRDS, REPTILES ETC.)!
Small animals - little knowledge!
There are 29 species of small mammals in Vorarlberg. These include representatives of the dormice, birch mice, true mice, shrews, voles, hedgehogs and moles.
We do not know much about the distribution of small mammal species in Vorarlberg. The available data is poor. But it is precisely this data that we need in order to compile the Vorarlberg Red List of Small Mammals. And that's not so easy - because many of the small animals live very hidden lives and are difficult to find. And this is where your cat comes into play. Its hunting instinct makes it a predator - and therefore a co-researcher for us!
The cat in the service of science
Around 24,000 cats live in Vorarlberg (Statistics Austria 2019/2020).
A cat brings home 1/10 of its prey. However, these "gifts" are not usually met with joy by humans and so the small mammals are disposed of as quickly and inconspicuously as possible.
Unfortunately, it has to be said. Because these prey animals provide valuable information. As dead animals, they can be clearly identified to species. Information on sex, body mass and reproduction can also be obtained from the respective species.
You can find information about our small mammals in Vorarlberg at www.laendlemaus.at (in German).
What is close to our hearts!
So that we are not misunderstood - we are expressly not encouraging you to "send your cat hunting" more often (if that is even possible)! But we do think that if mice and other small mammals are already dying, then their deaths should still have a benefit for scientific research.
Free-roaming cats prey on small mammals, amphibians, reptiles and birds. You can find out how you as a cat owner can enjoy your cat and protect birdlife at the same time at www.birdlife.at.
What data is required?
Your name, address, telephone number, e-mail address, date found.
Please use the report form (in German) and fill it out in pencil.
Only with this information can your dead small mammal be used scientifically!
When can dead small mammals be handed in?
From June to November 2024, dead small mammals can be handed in at inatura and at the drop-off points.
Where are the drop-off points? You can find the list of drop-off points on the project website.
Further information on the "Show me your mouse, cat!" project can be found on the project website.
The project is being realised by the nature museum inatura Erlebnis Naturschau Dornbirn together with apodemus OG - Privates Institut für Wildtierbiologie.
Project duration: June - November 2024
Project management:
Dr. Christine Resch, Dr. Stefan Resch, apodemus OG - Privates Institut für Wildtierbiologie www.apodemus.at
Project organisation:
Dipl.–Biol. Anette Herburger, Teamleitung Forschung der inatura Erlebnis Naturschau GmbH

This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.



