ServeToPe
Better governance of ecosystem services at local scales in the Wienerwald region
A joint research project of the University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna (BOKU) and the University of Vienna.
What is ServeToPe studying and what are its goals?
Society uses a variety of services that natural ecosystems provide, such as clean water, an attractive landscape for recreational purposes, food, or renewable energy sources. Many of these so-called ecosystem services (ESS) are influenced by humans. These include, for example, agricultural activities or the construction of roads. As a consequence, society regulates human actions and thus indirectly the availability of ESS. Examples of such policies are agri-environmental programs or local land use planning.
The Citizen Science project ServeToPe develops methods to better quantify the demand for ESS and their availability in a landscape. ServeToPe thus aims to contribute to more sustainable management of ESS and more targeted policies that focus on people's needs. ServeToPe is thereby based in the biosphere reserve Wienerwald as a case study region.
ServeToPe mainly aims to answer the following research questions.
- What is the current demand for ESS and to what extent can the Wienerwald region satisfy this demand with the offered ESS?
- What does "good management" mean from the citizens' point of view? How can policies contribute to a convergence of demand for ESS and their supply?
ServeToPe will reveal mismatches between the demand for ESS and their supply and will propose countermeasures. An example of this could be regional conservation efforts specifically planned for the landscape.
What methods are used?
ServeToPe uses a variety of methods to answer the research questions and to involve as many and as diverse citizens as possible. For example, workshops were held in schools or with citizens from the region. All citizens can participate online via a survey (see below). On the project website you can find more information about the methods and the roles of citizens (in German).
How can I participate?
Citizens are important research partners in ServeToPe. In particular, they support the visualization and quantification of the demand for ESS and of conflicting goals and trade-offs of between different ESS. A trade-off exists, for example, when several citizens want to use the same area for different purposes resulting in conflicts (e.g. recreational use and food production). You as citizen can therefore make an important contribution to the research project by participating in the following anonymous surveys.
In the main survey you can (1) enter your own activities and uses of ESS in the Wienerwald, (2) enter and locate frequently observed activities and ESS uses, and (3) identify trade-offs and opportunities for improvement. You can also upload pictures for this purpose. The main survey can be filled in only once.
However, you can also participate more regularly and thereby support ServeToPe even more intensively. This is possible via a second short survey, where you can enter and locate observed activities and ESS uses, as well as trade-offs. A picture upload is also possible here. In this short second survey, you can participate repeatedly over the entire duration of the project - i.e. continuously enter your observations. This gives us an even more accurate representation of uses and activities. You as a citizen scientist gain the opportunity to locate multiple uses and activities in areas and therefore identify multiple and more accurate trade-offs and improvements.
What happens to these results?
The results from the surveys of activities, uses, and trade-offs in the Wienerwald are compiled by the BOKU Vienna and University of Vienna research team and compared with other data on the supply of ESS (see methodology). These results are then published on the ServeToPe website. You can also sign up in our contact form to receive the results via email.
Afterwards, the results are presented to stakeholders from the region (e.g.: Employees of the administration, representatives from agriculture, nature conservation, recreational use, education and regional management) in a workshop. In this workshop, solutions and countermeasures will be developed based on the identified trade-offs and conflicts due to differences in ESS supply and demand.
If you have any questions, please contact Katrin Karner (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.) without hesitation.
The project team
ServeToPe is led by Martin Schönhart (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.) and Katrin Karner (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.), from the Institute for Sustainable Economic Development at BOKU University. Furthermore, the project team includes Thomas Wrbka (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.) and Florian Danzinger (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.) from the Department of Botany and Biodiversity Research at the University of Vienna. In addition, the students of the course " Conservation Related Methodologies of Social, Cultural and Economic Sciences" of the University of Vienna are involved in the project. If you have any questions, please contact Katrin Karner (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.) without hesitation.
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Phänoflex
Flexibilisation of WF-mowing dates according to the phenological model
The ÖPUL-measure Nature Conservation results in farmers usually having an agreement on a fixed mowing date. Due to the ongoing climate change, vegetation development fluctuates more and more especially during spring and early summer. Therefore, it was proposed to expand the flexibility of harvest date requirements. For this purpose, over a hundred farmers all over Austria started to observe the course of panicle development and the blooming of black elderberry. Based on this data, a phenological model is calculated for each region. During a warm year with an early onset of vegetation development, the farms can mow their meadows before the date given by the project confirmation. The new, earlier date is then communicated via www.mahdzeitpunkt.at.
Roles and responsibilities
Project lead
Austrian council for agricultural engineering and rural development
Project partners
GeoSphere Austria (former Central Institute for Meteorology and Geodynamics)
Modeling of the annual vegetation development with the additional inclusion of weather data from GeoSphere Austria. Analysis and handling of meteorological data and phenology data from GeoSphere in cooperation with experts.
LACON landscape planning consulting
Modeling of the annual vegetation development with the additional inclusion of weather data from GeoSphere Austria as well as annual organization and supervision of the observations by the Citizen Scientists.
Citizen Scientists
Monitoring and documentation of the phenology of cock's-foot and elder
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
C.S.I. PhänoBiota
Research with new plant aarivals from all over the world
DURATION: 01.05.2020 - 30.04.2023
In a first-of-its-kind approach in Europe, pupils in the district of Liezen are researching and documenting the phenological development of invasive neophytes under the influence of climate change. With the help of experts, they develop and test modern, multilingual field research instruments and educational tools, thus laying the foundation for a long-term, nationwide Citizen Science network. The observations are used to make neophyte management in the region more efficient, supported by phenological information. The project results thus not only have educational value, but also tangible ecological benefits.
What is happening in the project or has already happened?
In C.S.I. PhenoBiota, kindergarten children and pupils from all school levels in the Liezen district explore the exciting phenological world of neophytes together and at eye level with scientists. Equipped with comprehensive, age-appropriate research tools, they observe and document the phenological phases of selected plant species throughout the year, relate them to the climate and learn to draw professional conclusions. What is phenology? A large part of the material in C.S.I. PhenoBiota is developed together with the pupils. For example, a NawiTech research box for kindergarten children is being developed to make the project's main topics accessible to our youngest participants in a playful way and with all their senses. In the Girls only! programming course, schoolgirls develop a simple app.
.jpg)
Pupils observe with the Nature Calendar App © Marco Schupfer
With the help of the already existing nature calendar app and the new neophyte feature, parents, grandparents, siblings and other interested Citizen Scientists should also be encouraged to participate in the project and share their phenological observations. How does the app work (in German)? However, there is also an analogue way to record the phenological phases using observation sheets. Click here to download the sheets (in German). At the end of the project, the collected data will be used to create phenomenal hubs for all participating school classes, with the help of which our young researchers can forecast the annual development of neophytes in their region.
In addition, the pupils have the opportunity to work out and examine their own scientific questions that are of burning interest to them on the topic.
In the project, the young researchers accompany the entire process from the planning, development and implementation of phenological data collection to data evaluation and application of the findings. They also actively help to communicate their results.
Click here to listen to the radio programmes:
- Projektvorstellung C.S.I.PhänoBiota
- Radiosendung Phänologischer Frühling
- Schüler:innen machen Radio – Neophyten und Co
- Radiosendung Phänologischer Sommer
In keeping with the theme, our experts also come to schools and provide exciting insights into their professions. Pupils visit researchers in the region and make valuable contacts for the future. Interested students have the opportunity to write pre-scientific Matura papers on the topic and to work closely with our experts.
Excursion with the Naturschutzbund to the Trautenfels nature reserves © Marco Schupfer
Project goals
To get to know the complex of topics "Neophytes-Phenology-Climate Change" and to explore connections independently through innovative, interdisciplinary teaching methods. Enable and use access to NawiTech researchers in the region, e.g. for projects, internships, excursions, scientific work). Strengthen the role of children with a migration background through special tasks in the project and emphasise and use their competences.
Actively involve parents, grandparents, siblings and other interested Citizen Scientists in the project and get them enthusiastic about joint research.
Project partners
- Corporate partner:
- RML Regional Management Bezirk Liezen
- Scientific partners:
- Berg- und Naturwacht Steiermark
- Central Institute for Meteorology and Geodynamics
- Higher Federal Teaching and Research Institute for Agriculture Raumberg-Gumpenstein
- Educational institutions:
- WIKI Kindergarten Donnersbachwald
- Altenmarkt Nature Park Primary School
- St. Gallen Nature Park Primary School
- Primary School Aigen im Ennstal
- Secondary School Irdning
- Secondary School Stainach
- Admont Abbey Grammar School
- Federal Training College for Kindergarten Education Liezen
-nup-steirische-eisenwurzen-min.jpg)
Group photo of consortium partners © NUP Steirische Eisenwurzen
What opportunities does your project offer for educators who would like to apply for a cooperation grant?
We invite educational institutions from all school levels and from all over Austria to participate in the project through individual activities and to take a closer look at the fascinating phenological world of neophytes with us. All activities of C.S.I. PhenoBiota can also be implemented with cooperating schools. You are welcome to bring in your own ideas on the project topic and explore them together within the framework of the cooperation grants. Cooperation grants are awarded on a first come, first served basis.
Picture gallery
-
 Pupils sketching the neophytes © Marco Schupfer Pupils sketching the neophytes © Marco Schupfer
Pupils sketching the neophytes © Marco Schupfer Pupils sketching the neophytes © Marco Schupfer -
 Neophytes at first hand © Marco Schupfer Neophytes at first hand © Marco Schupfer
Neophytes at first hand © Marco Schupfer Neophytes at first hand © Marco Schupfer -
 Monitor neophytes and support science with the app © Marco Schupfer Monitor neophytes and support science with the app © Marco Schupfer
Monitor neophytes and support science with the app © Marco Schupfer Monitor neophytes and support science with the app © Marco Schupfer -
 Excursion to the HBFLA Raumberg-Gumpenstein © Marco Schupfer Excursion to the HBFLA Raumberg-Gumpenstein © Marco Schupfer
Excursion to the HBFLA Raumberg-Gumpenstein © Marco Schupfer Excursion to the HBFLA Raumberg-Gumpenstein © Marco Schupfer -
 Rhizome box to try out © Marco Schupfer Rhizome box to try out © Marco Schupfer
Rhizome box to try out © Marco Schupfer Rhizome box to try out © Marco Schupfer -
 Tracking neophytes © Sabina Kropitsch Tracking neophytes © Sabina Kropitsch
Tracking neophytes © Sabina Kropitsch Tracking neophytes © Sabina Kropitsch
https://www.citizen-science.at/en/immerse/dates/tag/plants?start=10#sigProIddc2722188d
Mit Unterstützung vom Bundesministerium für Klimaschutz, Umwelt, Energie, Mobilität, Innovation und Technologie sowie die Österreichische Forschungsförderungsgesellschaft (FFG) mit dem Förderschwerpunkt Talente regional.


This project fulfilled version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
City Nature Challenges in Austria
Every observation counts!
The City Nature Challenge (short: CNC) is an annual nature competition between regions that takes place in spring (usually at the end of April, beginning of May) and is held simultaneously in various cities and regions worldwide. On four consecutive days, people around the world document the diversity of wild animal, plant and fungi species in their region using photos and sound recordings and share them on iNaturalist. Together with others the observations are then identified to species level on iNaturalist.
The CNC was invented by the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County and the California Academy of Sciences in 2016 and is organized by them since then annually. 2018 the CNC went globally, and hundreds of cities and regions are participating since then in this friendly challenge every year: Which region makes the most observations? Which region has the most species? Which region can motivate the most participants?
All observation of wild organisms in the participating regions count!
Since 2020, several Austrian cities and region are also participating in this international event. The CNC is organized by each of the participating cities or regions on their own. The “City Nature Challenges in Austria” project acts as an umbrella project for these participating cities and regions in Austria.
The aim of the CNC is to reacquaint people with their local biodiversity, to arouse curiosity and to discover nature on their doorstep. You can use the observation platform iNaturalist to exchange ideas with other nature lovers and learn and improve your knowledge of the species by identifying species together with others. This data helps research, administration, and nature conservation: it contributes to a better understanding of the status of species and their distribution in Austria. Due to the large number of observations, robust data on phenology can be obtained, area expansions of invasive species or of rare/sensitive species can be detected, and rediscoveries and new finds are also possible.
When?
The next City Nature Challenge takes place from April 25th to 28th 2025. Planning for the 2026 CNC event already starts in autumn 2025.
Participate
Everyone can participate in the City Nature Challenge by making observations or help identifying observations to species level! No registration to the project is necessary. All you need is a camera (smartphone or digicam) and a free iNaturalist account for uploading the photos. In Salzburg and Vorarlberg, Observation.org and the ObsIdentify app are used to collect data. The use of both platforms is free of charge.
Now, simply take photos of wild animal, plant or fungi species between April 25th and 28th 2025 in the participating regions and post them on iNaturalist. That is all it takes for your observation to count in the City Nature Challenge!
You can also help identify species on iNaturalist submitted during the CNC. Or simply tell your family, friends or colleagues that the CNC is happening in their region.
iNaturalist is a citizen science platform where everyone can post images or sound recordings of their species observations and identify it together with other users. It is run by the California Academy of Sciences and the National Geographic Society. Beside the documentation of biodiversity users can also get in exchange with each other over the platform.
In Austria, you can take part in the City Nature Challenge in 2025 in the following regions:
- Amstetten – Waidhofen/Ybbs
- Elsbeere Wienerwald
- Graz bis Vulkanland
- Industrieviertel
- Innsbruck
- Krems – Wachau – Melk
- Marchegg
- Mittelkärnten
- Nationalparkregion Gesäuse
- Neusiedler See/Seewinkel
- Salzburg (via observation.org)
- St. Pölten
- Vorarlberg (via observation.org)
- Wien
What’s with the data?
The observations reported to iNaturalist during the course of the CNC can be viewed and used by any user of the observation platform. So they are freely available. In addition, verified observations (which have the status of "research grade") are shared with GBIF "Global Biodiversity Information Facility" – an international biodiversity database – used by scientists worldwide for their research. In addition, the observations are also available in the Austrian Biodiversity Atlas with a slight delay.
Through your iNaturalist account, you can control how your observations and photos may be used (by providing a Creative Commons license) and you can also remove your observations at any time by deleting your account.
Podcast episode
In April 2023, coordinator of the region Krems-Wachau-Melk, Tanja Lumetsberger, presented futher insights and details about the City Nature Challenge in our podcast Wissen macht Leute. You can listen to the episode here (in German).
Further information
Further information on the City Nature Challenges in Austria and how you can be part of it can be found on our project website.
Information on the official international project can be found at www.citynaturechallenge.org (in English).
Implementing organisations
- Haus der Natur Salzburg
- Haus für Natur, Museum Niederösterreich
- inatura Vorarlberg
- Institut für Biologie, Universität Graz
- Nationalpark Gesäuse
- Nationalpark Neusiedler See – Seewinkel
- Naturhistorisches Museum Wien
- Naturwissenschaftlicher Verein für Kärnten
- Paris-Lodron Universität Salzburg
- Tiroler Landesmuseen
- Universalmuseum Joanneum
- Universität für Weiterbildung Krems
The City Nature Challenge is organized on a global scale by the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County and the California Academy of Sciences.

This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Looking for Cowslips
In spring, scientists invite everybody around Europe to take part in the biggest cowslip observation campaign “Looking for Cowslips”. The aim of the project is to examine the patterns of flower morphological traits (i. e. heterostyly) in cowslip populations all across Europe using a citizen science approach. The citizen science project “Looking for Cowslips” was carried out already in 2019 and 2020 in Estonia and Latvia. Within the frames of this campaign, we obtained heterostyly data from > 150 000 cowslip individuals in each year of 2019 and 2020 in Estonia (and Latvia). Since 2021 we are also asking enthusiastic citizen scientists across the EU to participate and contribute, with great success. Data originating from the campaign provides unprecedented insight into the patterns of heterostyly following the loss of semi-natural grasslands.
Participants are expected to observe the patterns of heterostyly in cowslips. The cowslip (Primula veris) is a heterostylous plant – it means that the plant can have one of the two types of flowers. These different types of flowers are called S-morphs (short-styled) and L-morphs (long-styled). In short-styled cowslips (S-morphs), five anthers are visible in the flower when looking from above, and in individuals with L-type flowers, a green dot in the middle of the flower (the stigma) is visible. Normally in cowslip populations, the frequency of these different types of individuals is more or less equal. Imbalance reduces a plants’ opportunities to find a suitable mate for reproduction, which impedes pollination and the exchange of genetic material. This, in turn, reduces a plants’ vitality. The cowslip’s regular habitats – traditionally managed grasslands – have become increasingly rare in the contemporary landscape. The disappearance of grasslands causes decline in plant populations depending on grassland habitats. A massive decline in cowslip populations can cause substantial imbalances in the frequency of L- and S-morphs to the extent that one of those types completely disappears from the habitat. That is precisely the kind of a possible shift in the balance between the L- and S-morphs caused by changes in the landscape that we want to study – with your help. An observation takes about 30 minutes. When possible, one should observe the flowers of 100 cowslip individuals. Look at the flower and report whether you see five anthers (S-morph) or one stigma (L-morph). Find the time, breathe some fresh air, and help scientists with their work!

For more information, check out our webpage www.cowslip.science.
To find out more about the interesting findings from the first year of the campaign, you can read the article at: https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1365-2745.13488.
You can contact us at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. for further questions.
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
PolliDiversity 2.0
Compared to PolliDiversity, PolliDiversity 2.0. is still about creating habitats for insects, but the tasks of the citizen scientists have changed somewhat due to usability. The project was offered for the first time at the Citizen Science Award in 2021. In 2022, the second round took place in a modified form. Due to career changes of the project participants, the project will not be offered in 2023, but further project runs are planned for the future.
The aim of PolliDiversity 2.0. is to get as many people as possible excited about biodiversity and pollinators in their environment. Through active participation in research, the intrinsic motivation to actively engage in biodiversity conservation can be promoted. The goal of the citizen scientists will be to document the phenological development of plant species and then observe which pollinators visit these areas and at what time.
What are the tasks of the participating citizen scientists?
The main task of the citizen scientists is to document how the different plant species in the ReNatura wildflower mixture Gumpensteiner BW3 develop phenologically. Another task will be to observe the pollinators that visit the flowering areas. The resulting data will on the one hand provide interesting insights into the plant species in the flowering mixture and on the other hand valuable contributions to research into the lifestyles of the pollinators.
Documentation of phenological development
For the documentation of the phenological development of the flowering areas, a template is handed out to the citizen scientists to be completed for the documentation. The time of sowing, budding, flowering and plant growth should be documented. Different parameters such as outdoor temperature, weather and altitude are also included.
Observation of pollinators and data collection
When observing pollinators, the focus should be on wild bees in particular. Participants will also be given a simple identification key to assist them. Data collection is done via the platform of the Austrian Nature Conservation Union www.naturbeobachtung.at. There is a separate comment function where the project "PolliDiversity 2.0" is to be indicated.
Planting the flowering area
Citizen scientists receive seeds of the ReNatura wildflower mixture Gumpensteiner BW3 for an area of approx. 5 m². The seeds can be sown in your own garden or optionally in pots, which is why it is also possible to participate without having your own garden. The following plant species are sown:
Yarrow (Achillea millefolium), Field chamomile (Anthemis arvensis), Dyer's chamomile (Anthemis tinctoria), Kidney vetch (Anthyllis vulneraria), common marigold (Calendula officinalis), Caraway (Carum carvi), Cornflower (Centaurea cyanus), Brown Knapweed (Centaurea jacea), Centaurea pseudophrygia, Scabiosa (Centaurea scabiosa), Common Chicory (Cichorium intybus), Meadow Buttercup (Crepis biennis), Wild Carrot (Daucus carota), Carthusian Carinthia (Dianthus carthusianorum), Viper's Head (Echium vulgare), Widow's-flower (Knautia arvensis), Dandelion (Leontodon hispidus), Marguerite (Leucanthemum vulgare), Kidney Clover (Lotus corniculatus), Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla), Yellow Clover (Medicago lupulina), White Sweetclover (Melilotus albus), Sweet Yellow Clover (Melilotus officinalis), Evening Primrose (Oenothera biennis), Sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia), Corn Poppy (Papaver rhoeas), meadow sage (Salvia pratensis), red campion (Silene dioica), common glue (Silene vulgaris), hare clover (Trifolium arvense), field clover (Trifolium campestre), small clover (Trifolium dubium), red clover (Trifolium pratense), black mullein (Verbascum nigrum), Sticky Catchfly (Silene viscaria) - all certified according to G-Zert®.
In the best case, the flowering area should be established as early as March (as soon as the first early flowering plants become visible), but by the end of April at the latest.
Which materials will be made available to the participating citizen scientists?
In order to enable citizen scientists to identify and participate in the project, the following information materials will be prepared and made available in digital form:
- Info workshop on Zoom
- Digital materials for participants: Experiment instructions, information materials on pollinators and identification keys for the selected pollinators.
- Template for the documentation of phenological development
The project materials are only available in German.
Further details on the project
The task of the citizen scientists is to document how the flowering areas develop: When do the seeds emerge? What is the temperature? What was the weather like in the past weeks? How tall are the plants after another two weeks? When do the first plants start to flower? If no plants come up, what could be the reason - have birds or snails been seen?
Furthermore, the citizen scientists should determine on several days from May to the end of July (depending on the flowering time of the plants) which plant species is preferred as a food source by certain wild bee species and other pollinators. Monitoring should be carried out on as many days as possible at three different times of day during daylight hours. The weather also plays a role, as wild bees are more likely to be seen in sunny weather but less likely to be seen in rain or strong winds.
How will the data of the participating citizen scientists be handled?
The data will be treated strictly confidentially and in accordance with the EU General Data Protection Regulation.
How can interested parties register?
Interested parties are welcome to register by e-mail. Please send registrations and queries to: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Citizen Science Seminar
In 2021, poject coordinator Verena Mayer held a lecture about "PolliDiversity" as part of the lecture series "Citizen Science Seminar" at the University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences Vienna (BOKU): "'PolliDiversity' - pollinator diversity in your own environment" (in German).
Project coordination:
Mag. Verena Mayer
Dipl. Ing. Renate Mayer
Other contributors:
Dr. Wilhelm Graiss
This project fulfilled version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Pollen Diary
The Pollen Diary was launched back in 2009 as a scientific project as part of a master's thesis at the WU Vienna Executive Academy. Meanwhile it has become an important service for pollen allergy sufferers in 13 European countries: Austria, Germany, Switzerland, France, Great Britain, Sweden, Finland, Croatia, Hungary, Lithuania, Serbia, Slovenia and Turkey. The number of users is growing every year, not at least because of the projects that were made possible by the Pollen Diary, such as the pollen app, the exposure map and the personalized pollen information.
Users have the possibility to document their own allergic complaints (intensity and symptoms) together with their medication intake. This gives an overview of the pollen allergy and allows them to compare the symptoms with the measured pollen concentrations on a continuous basis as well as at the end of the stress phase of the allergy. In addition, it is possible to download an excel file with all entries. There, all data are summarized and additionally correlation calculations of pollen count and symptoms are provided. This is a first step towards the identification of the trigger. And even after the diagnosis by a specialist, the pollen diary is a valuable support for patients and medics to track the success of a therapy, the administration of medication or the course of the pollen allergy.
To make such a service possible in the first place, the Pollen Diary is linked to the European pollen database, and can therefore be used without any problems in all countries where it is already available. Special attention has been paid to easy handling as well as to compliance with the latest EU directives on data protection (more under the terms of use of the Pollen Diary).
Since 2013, the pollen diary can also be accessed via the "Pollen" app on Android and iOS. If a user documents complaints, a personalised pollen forecast is available free of charge, tailored to the personal reaction profile. Via the app, users can also get the stress forecast and other practical helpers for the everyday life of an allergy sufferer, which are offered free of charge on the homepage of the Austrian Pollen Warning Service.
Europe-wide pollen information is reached via this portal: www.polleninfo.org.
Image gallery
https://www.citizen-science.at/en/immerse/dates/tag/plants?start=10#sigProIdb081d519a9
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Homegrown
“Homegrown - There is nothing like a homegarden”
Project description
With their variety of plant species and the experience of the gardeners, rural home gardens constitute an integral component of the cultivated landscape in the Lienz district, East Tyrol. Together with pupils of the BG/BRG Lienz school (and biology, math/physics and English teachers), scientists are investigating rural home gardens, including stocks of plant species and the use of plants. These results will be compared with those taken 20 years ago from the same gardens and will help to identify changes in gardens and their cultivation. These diachronic perspectives allow a precise and empirically established overview of changes in rural home gardens in the countryside of an industrial and services-focused state, in the context of demographic and economic changes and the search for a new identity.
To gain a better understanding of the local perception of the significance of rural home gardens, observations from gardeners and their neighbours concerning ecosystem services in gardens and their significance will also be recorded.
The project will also investigate cultivation techniques that adapt to extreme weather or ensure sustainable growth. It will also find out why people grow gardens and which values and approaches guide their behaviour or actions in gardens.
As part of an additional citizen science module, the local population in East Tyrol and Oberen Drautal will be combined. The module appeals to gardeners who are interested in taking surveys in their gardens, according to methodological direction and by monitoring their gardens, so as to demonstrate the material and immaterial ecosystem services in gardens. These gardeners and the cooperating young people will be trained in simple quantitative and qualitative survey methods for this purpose. This will take into account the opportunities that depend on the education and experience of each individual participant.
The starting point for developing analogue survey tools for the researching gardeners is a universal T-card office planner (49 x 47.3 cm, 7 panels, light grey) with 20 slots and 7 columns. The card slot system provides a weekday structure (Monday to Sunday), an hourly structure (6 a.m. to 10 p.m.) and six variables for recording ecosystem services.
On the universal T-card planner, the gardeners use the provided weekday and time scales with differently coloured slots to record the following specific information in writing about the individual ecosystem services during the recording period:
- Provisioning services, such as the yield of vegetables and fruits from the home garden (name of the person harvesting, time and duration, name of the harvested fruits and vegetables, the amount harvested and its respective use).
- Regulating services, such as birds, insects or pests in the home garden (name of the observing person, time and duration, name and number of birds, insects or pests observed).
- Cultural services, such as cultivation techniques in the home garden (name of the person cultivating, time and duration, tools used, etc.) or activities in the home garden when used as a place for relaxation and leisure.
The time spent in the garden will be recorded with a simple stopwatch. Some plant materials will be weighed out with simple, easily available kitchen scales. The card slots will be placed somewhere protected from weather or positioned where they are in the gardener’s view. This location will be decided on site with the gardener.
The duration of collections using the card slot system will be calculated at at least a week and will then be passed on to another gardener. Seven card slot systems will be prepared. The recordings ran from 1 August to 31 August 2018.
Through the participation of citizen scientists, a continuous observation and record of local perception (emic viewpoint) of the ecosystem services of home gardens is guaranteed. The methods were proposed by a gardener from the region being researched and were discussed/considered together with other gardeners from the area. The citizen scientists were actively involved in data acquisition and collection, data analysis and interpretation and the publication of results in the project report, scientific journals and conferences and in local media (dolomitenstadt.at). The collected data was continuously documented and stored by scientific guardians. Interim and final results were returned to the participating gardeners as part of the “give back” culture in the citizen science final event (“Gartenfest”).
Project collaborators
Heidemarie Pirker
Brigitte Vogl-Lukasser
Partners
BG/BRG Lienz (Renate Hölzl, Arno Oberegger, Hansjörg Schönfelder and the pupils of class 6b (from academic year 2018/2019: 7b).
Marie-Luise Wohlmuth (workshops on soil biology)
Ramona Walder (photography)
Peter Werlberger (video)
Gerhard Pirkner (dolomitenstadt.at)
Germain Weber & Team (Faculty of Psychology, University of Vienna)
Christian Ragger (REVITAL - Integrative Naturraumplanung GmbH)

Image gallery
(Click on an image to enlarge)
https://www.citizen-science.at/en/immerse/dates/tag/plants?start=10#sigProId537f10b2da
This project fulfilled version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Ragweed Finder
The Ragweed Finder was developed in 2017 by the Austrian Pollen Information Service at MedUni Vienna and has also been available to download as an app for Android and iOS since 2019.
The Ragweed Finder consists of four components:
- Specimen report
- Ragweed distribution map
- Information about Ragweed
- Manual to recognize ragweed
Specimen report
The most important data such as location, population size and symptoms can be entered quickly using the specimen report. Uploading a photo is mandatory, otherwise a reported specimen cannot be verified by the experts of the Ragweed Finder team. Users can decide whether to report by name or anonymously (only via email address).
Ragweed distribution map
Already verified specimen reports of ragweed are listed herein within the current season. The number of symbols amounts to the number of reports displayed on the map. The colouring around the specimen sites indicate the symptom intensity.
About Ragweed
What is ragweed? Where does it grow? What is known about ragweed pollen allergy? What can be done? These and other questions are answered in this compilation of the most important information about ragweed.
Recognize Ragweed
Some ragweed pollen allergy sufferers do not know their allergy trigger and may walk along an infested field without recognizing the plant. However, in order to report ragweed, a reliable identification of the plant is required. Many photos as well as a short instruction on how to take convincing pictures turns the interested citizen into a ragweed expert.
What happens with the specimen reports?
First of all, the specimen reports have to be evaluated. Each verified report is then transferred to the distribution map. Users will be informed about the evaluation of their specimen report via e-mail. The verified specimen reports are forwarded once a week to the responsible institutions/federal state governments. This enables the authorities to set appropriate corrective actions (e.g. mowing) and locate ragweed hotspots.
So far, there is no comprehensive legal obligation to report or remove ragweed in Austria. Only in Burgenland a law to control and prevent the spread of ragweed was passed in 2021.
Highlights:
- For the first time, a tool for recording ragweed plants is available free of charge for all of Austria.
- The ragweed distribution map is available for the public.
- Thanks to a guideline and a checklist for reporting ragweed specimen, anyone can identify and report ragweed.
Ragweed pollen allergy sufferers can be an active support to contain the uncontrolled spread of ragweed!

This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.
Citree
With the Citizen Science Project "CITREE" a crowdsourcing instrument for monitoring the growth of urban trees, will be developed and used. It builds on the "Sparkling Science" project "Woody Woodpecker", which deals with the growth, structure and function of wood.
Urban trees fulfill a variety of functions, such as improving the microclimate and air, noise protection or the design of public spaces. Monitoring of urban trees is important because climate change leads to an intensification of stress on the trees. In cities, trees are exposed to extreme heat and drought and are additionally affected by other stress factors such as pollutant emissions, limited root space, salt stress or pest infestation. Therefore, trees in cities are "living laboratories" that allow analyses of stress mechanisms and estimates of future developments. CITREE is intended to provide a tool for monitoring urban trees and thus create a bridge between citizens and their trees: On the one hand citizens can participate in the monitoring process, on the other hand they can see and learn how their trees grow. This feedback will also be used to present the work of public institutions (e.g. city nurseries) and will enable school projects on urban trees and urban ecology.

CITREE is based on easy to install and cheap band-dendrometers, with which the trunk circumference and thus the growth can be measured. Dendrometers installed on urban trees are read by citizens who have access to the CITREE database via QR code and smartphone. The CITREE database collects the growth data of all trees and makes it available to involved citizens, the public, public institutions and researchers.
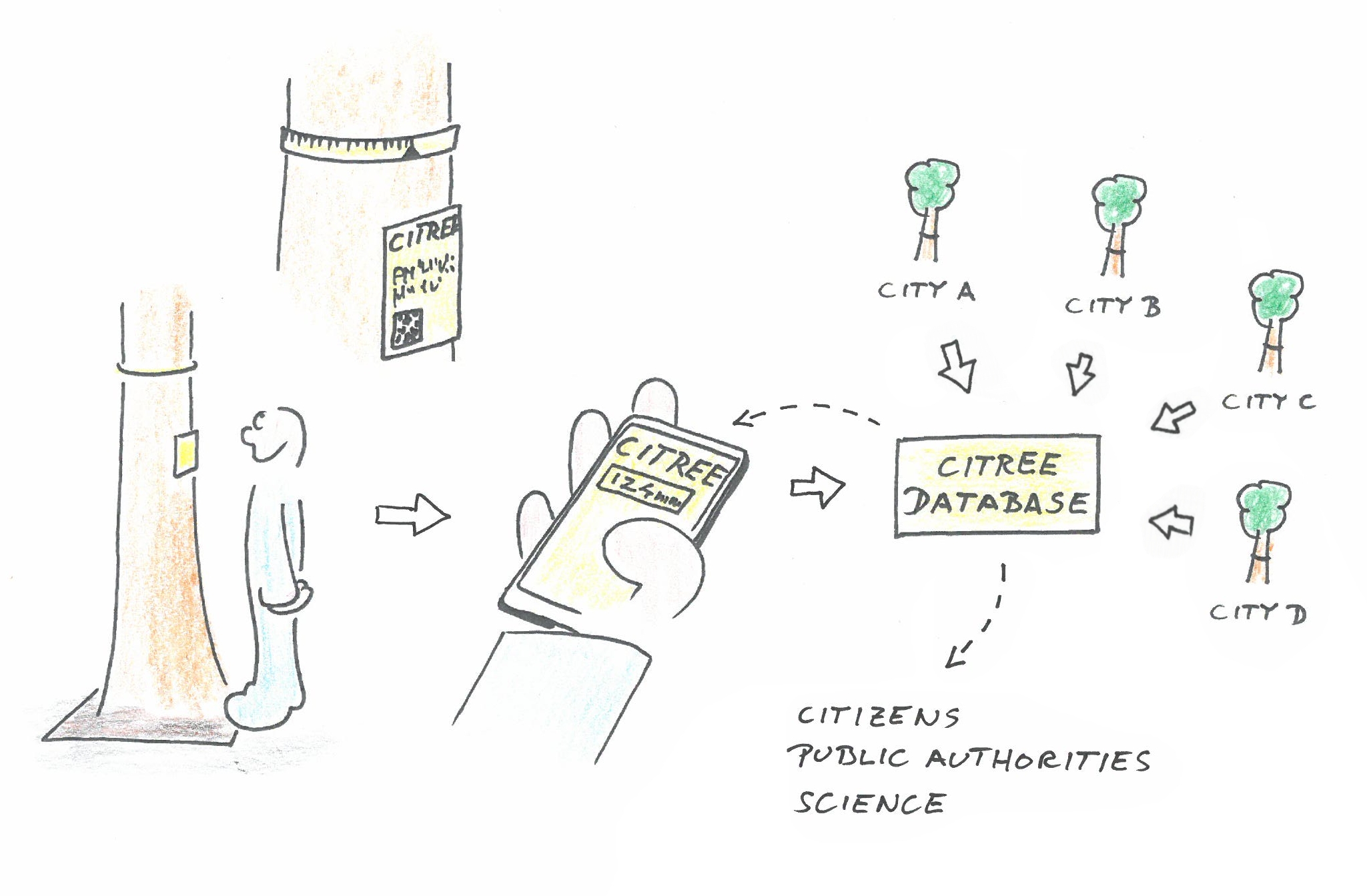
The main work packages of the project are:
- Selection/modification of suitable dendrometers
- Development of an installation system
- Development of the CITREE database
- Test and optimization of the developed systems under urban conditions
- Data analysis and
- Installation of the systems in Austrian cities.
The project will be carried out at the Institute of Botany, University of Innsbruck and will benefit from the long experience in the field of science communication of the PI (Stefan Mayr) and his staff. The development of the CITREE database is carried out in cooperation with the University of Ghent and the company Phyto-IT, Belgium. A cooperation with the School of Education, University of Innsbruck serves the didactical optimization. For the installation in Austrian cities, city nurseries and researchers will be contacted to collect a first broader data set on the growth of urban trees. In the long term, CITREE is to be further developed into CITREE-EU, thus enabling a monitoring network in European cities.
Tasks and roles in the project:
- Citizen Scientists:enter the numbers read from the dendrometer and receive a graphical display of the calculated tree diameter including the previous history.
- Tree patrons: Select trees, install dendrometers according to instructions, collect information on the location and condition of these trees. Can download the records of the database.
- Research assistants: handle special cases (resetting dendrometer, removing obvious mismeasurements...), tracking patterns of growth, vandalism, etc.
- IT-assistant: Creating new trees in the database and on the homepage
If you have any questions about the project, or are interested in participating in the project, please write to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
This project fulfils version 1.1 of the quality criteria for citizen science projects on Österreich forscht.





